In this blog, we’ll cover three fundamental concepts: operators, conditionals, and getting user input with the input() function. By the end, you’ll have a good grasp of how to use them in your Python programs.
What Are Operators?
Operators are symbols that tell the computer to perform specific mathematical or logical operations.
Think of them as the verbs in a sentence that tell you what action to take. There are several types of operators in Python:
Arithmetic Operators
These operators perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Addition (+): Add two numbers.

- Subtraction (-): Subtracts one number from another.

- Multiplication (*): Multiplies two numbers.

- Division (/): Divides one number by another.
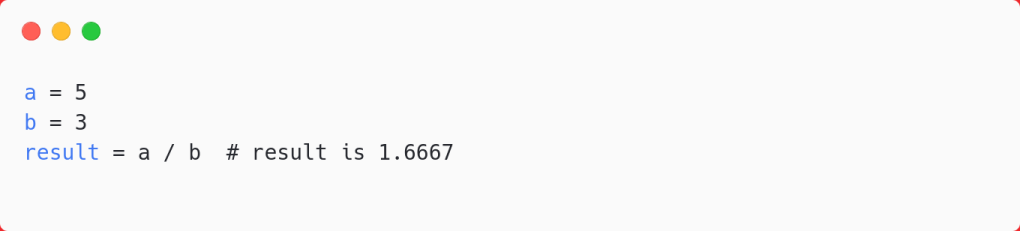
- Floor Division (//): Divides one number by another and rounds down to the nearest whole number.

- Modulus (%): Returns the remainder when one number is divided by another.

- Exponentiation ():** Raises one number to the power of another.

Comparison Operators
These operators compare two values and return either True or False.
- Equal to (==): Checks if two values are equal.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a == b) # result is False
- Not equal to (!=): Checks if two values are not equal.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a != b) # result is True
- Greater than (>): Checks if one value is greater than another.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a > b) # result is True
- Less than (<): Checks if one value is less than another.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a < b) # result is False
- Greater than or equal to (>=): Checks if one value is greater than or equal to another.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a >= b) # result is True
- Less than or equal to (<=): Checks if one value is less than or equal to another.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a <= b) # result is False
Logical Operators
These operators are used to combine conditional statements.
- and: Returns
Trueif both statements are true.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a > b and a > 0) # result is True
- or: Returns
Trueif one of the statements is true.
a = 5
b = 3
result = (a > b or a < 0) # result is True
- not: Reverses the result, returns
Falseif the result is true.
a = 5
result = not (a > 0) # result is False
What Are Conditionals?
Conditionals are like traffic signals for your code. They help your program decide which path to take based on certain conditions. The most common conditional statements in Python are if, elif, and else.
1. The if Statement
The if statement checks a condition and executes the code block if the condition is True.
a = 5
b = 3
if a > b:
print("a is greater than b")
2. The elif Statement
The elif statement is short for “else if”. It checks another condition if the previous if condition was False.
a = 5
b = 5
if a > b:
print("a is greater than b")
elif a == b:
print("a is equal to b")
3. The else Statement
The else statement catches anything that isn’t caught by the preceding conditions.
a = 3
b = 5
if a > b:
print("a is greater than b")
elif a == b:
print("a is equal to b")
else:
print("a is less than b")
Using input() to Get User Input
This function allows you to get input from the user. It’s like asking a question and waiting for the user to answer.
The input you get is always a string (text), so if you need a number, you have to convert it.
Basic Usage of input()
Here’s a simple example:
name = input("What is your name? ")
print("Hello, " + name + "!")
In this example, the program asks the user for their name and then prints the same.
Converting Input to Numbers
If you want to work with numbers, you’ll need to convert the input from a string to an integer or a float.
age = input("How old are you? ")
age = int(age)
print("You are " + str(age) + " years old.")
Putting It All Together
Let’s combine operators, conditionals, and input() in a simple example. Suppose you want to create a program that checks if a number entered by the user is positive, negative, or zero.
number = input("Enter a number: ")
number = float(number) # Convert the input to a float
if number > 0:
print("The number is positive.")
elif number < 0:
print("The number is negative.")
else:
print("The number is zero.")
In this example, the program:
- Asks the user to enter a number.
- Converts the input to a float (to handle decimal numbers).
- Uses conditionals to check if the number is positive, negative, or zero, and prints the result.
Quiz
Tasks:
Notebook:
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1pt0t51u7EM5uAHf_3uNUnbIqogd5Cv47?usp=sharing
